Solutions for Thermal Lancing Dust Control
If your operation involves thermal lancing—whether for heavy equipment manufacturing, steel fabrication, or infrastructure construction and repair—you need an air quality strategy that meets the challenges head-on. RoboVent engineers industrial dust control systems that keep workers safe, meet regulatory requirements and adapt to the real-world demands of heavy industry.
RoboVent brings deep experience designing systems for harsh, high-volume industrial applications like thermal lancing. Our engineers understand that effective dust and fume control for thermal lancing isn’t one-size-fits-all—it’s about crafting a tailored solution that works with your facility layout, production processes and compliance needs. RoboVent Senturion™ is our toughest dust collector, built to handle heavy dust and fumes. Whether you need a centralized dust collector for a traditional ducted push-pull ambient system, ductless floor-mounted ambient air filtration systems or a targeted solution for a specific zone, we can design a system to fit. We integrate explosion protection, fire suppression and safety systems for a safe, compliant solution. And with our computer-aided VentMapping® Engineering Process, you are guaranteed a solution that keeps your facility safe and compliant.
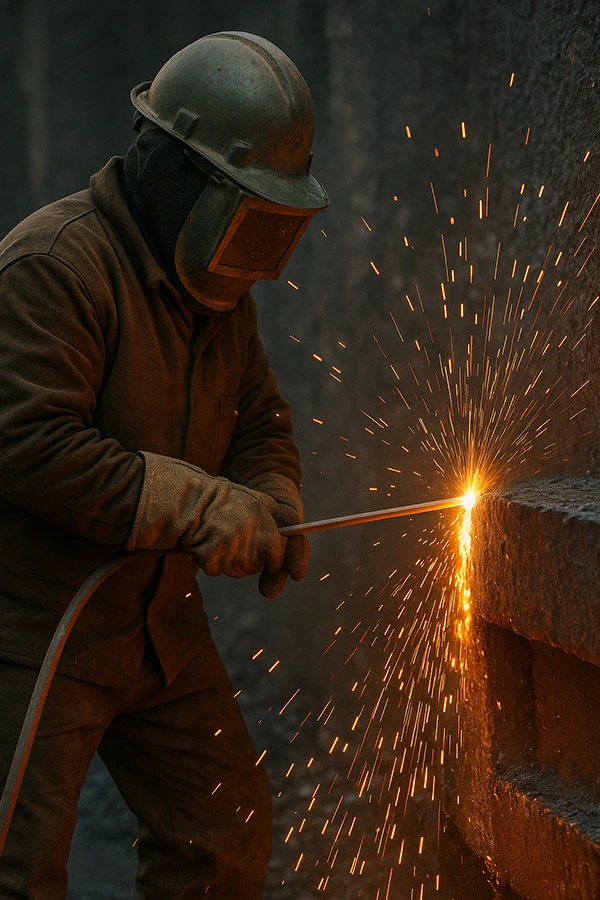

Thermal lancing produces extreme heat and heavy smoke.
Air Quality Challenges in Thermal Lancing
Thermal lancing produces intense, localized heat and rapid material oxidation—ideal for cutting thick metal or concrete, but problematic for air quality. Thermal lancing creates several worker health and safety challenges.
- Fume and Particulate Generation: The vaporization and oxidation of materials like carbon steel, stainless steel and alloy components during thermal lancing releases high concentrations of airborne metal fumes and ultrafine particulates. These fumes can contain hazardous substances such as iron oxide, chromium, manganese and nickel—commonly found in construction and transportation equipment manufacturing materials. Thermally generated fumes from thermal lancing are usually in the sub-micron range, meaning they can be inhaled deeply into the lungs and make their way to other body systems.
- Toxic Gas Emissions: Oxygen-rich cutting environments can generate nitrogen oxides (NOx), ozone and other harmful gases, particularly in enclosed or poorly ventilated areas.
- Sparks and Combustible Byproducts: Lancing operations produce hot slag, sparks and molten debris. In facilities working with combustible metal dust or coatings, this introduces significant fire and explosion hazards, which are intensified by the oxygen-rich atmosphere used in oxygen lancing.
Health and Safety Considerations for Thermal Lancing
Thermal lancing (much like hand plasma cutting) is often performed in large-scale industrial environments—such as railcar fabrication shops, scrap yards or construction equipment manufacturing facilities—where exposure risk is high due to open layouts and mobile work. Because it is a manual process, health and safety risks are high. This includes visual and auditory stressors due to the extreme brightness and loud noise of thermal applications, along with high risk for burns from molten metal, extreme heat and flying debris.
Thermal lancing health and safety concerns also include significant exposure risks from inhalation of thermal lancing fumes, which can lead to acute conditions like metal fume fever and long-term respiratory issues. These risks are escalated in thermal lancing due to the high speed and heat of the procedure and the thickness of the material. Lancing operations result in high levels of small, fumed particulate from the high heat of the process, which can be inhaled deep into the lungs. Toxic substances found in stainless or chromium-alloyed steel—such as hexavalent chromium, cadmium, nickel and manganese—are known to create health risks such as:
- Metal fume fever, flu-like symptoms from acute inhalation of metal oxide fumes.
- Lung cancer associated with exposure to hexavalent chromium and nickel compounds.
- Chronic respiratory disease, including bronchitis and reduced lung function.
- Neurological effects, including Parkinson’s-like symptoms and manganism, linked to prolonged exposure to manganese.
- Skin and eye irritation caused by direct contact with fumes or particulates.
- Respiratory sensitization, with increased risk of asthma or allergic responses.
Regulatory Compliance for Thermal Lancing
As manufacturers expand or modernize facilities to support reshoring, thermal lancing operations must be designed with today’s air quality and safety standards in mind. This high-heat, high-particulate process presents unique compliance challenges for worker health, fire safety and environmental emissions.
- Worker Health and Safety: Thermal lancing generates hazardous metal fumes, including iron oxide, manganese, nickel and hexavalent chromium. Employers must comply with Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) permissible exposure limits (PELs) and implement controls to protect workers from acute and chronic health risks. NIOSH and ACGIH also provide recommended best practices and exposure limits, which may be lower than the OSHA PEL.
- Combustible Dust: Fine, hot particulates from lancing operations and other nearby metalworking processes can create fire and explosion hazards if not properly managed. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) publishes internationally recognized standards for fire and explosion safety, including combustible dust safety and dust control system design. NFPA 660 outlines requirements for dust hazard analysis (DHA), spark arrestance, explosion venting, and isolation systems in combustible dust environments; dust collection systems must also comply with NFPA 68 (Explosion Protection by Deflagration Venting) and NFPA 69 (Explosion Prevention Systems).
- Environmental: Facilities must also consider U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Clean Air Act requirements for emissions of hazardous air pollutants (HAPs) and VOCs. Proper dust and fume collection, along with effective filtration, helps control emissions and support environmental compliance.
Considerations in Dust and Emission Control for Thermal Lancing
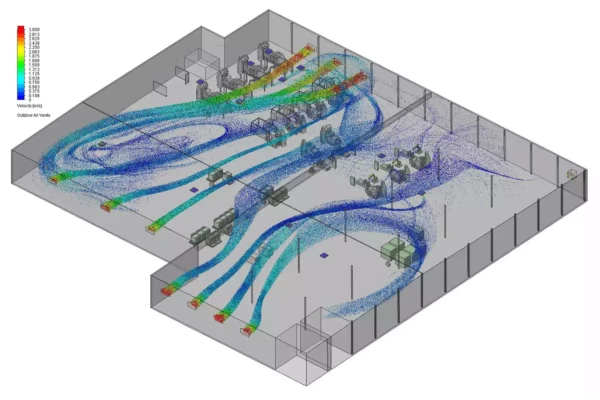
Because thermal lancing is typically performed manually on large components in open, high-heat environments, source capture is often not feasible. Operators need to move freely around massive structures—such as equipment frames, railcar assemblies or structural steel elements—and the intense heat and molten slag generated during lancing make it difficult to position extraction close to the arc. In these cases, ambient air filtration systems provide a reliable and scalable solution for controlling airborne contaminants across the entire work zone. Ductless systems like RoboVent Vortex are especially effective in facilities that use overhead cranes, have tall ceilings or rely on large workstations that can’t be easily enclosed.
Where it’s possible to safely position localized capture—such as in semi-contained prep or repair areas— fume arms with heat-resistant hoods can help remove metal fumes and particulates at the source.
Other key considerations in air filtration for industrial cutting include:
- Spark arrestance: Thermal lancing and industrial cutting produces a constant stream of hot sparks, slag, and molten metal. All systems must be carefully engineered with spark arrestance systems, such as the Delta3 Inline Spark Arrestor.
- Fire and explosion protection: If metal dust or particulate accumulates in the system, it can pose a serious combustible dust hazard, especially during high-heat processes like thermal lancing. Materials such as aluminum, magnesium and coated metals are particularly reactive and require extra precautions. Dust collection systems must be equipped with explosion protection and active dust collector fire suppression systems to mitigate the risks of deflagration and fire events. System design should comply with the latest guidance under NFPA 660.
- Filter selection: The intense particulate load and high fume concentration produced by thermal lancing demand high-efficiency, durable dust collector filter cartridges. For fine or hazardous particulates (e.g., hexavalent chromium), HEPA after-filters or specialized gas-phase filtration (e.g., activated carbon) may be needed to meet OSHA exposure limits and protect recirculated air. Because of the extreme heat and spark risk, filters should also feature flame-retardant media to reduce the chance of ignition and improve system safety.
- Airflow requirements: Proper airflow is critical to maintaining a safe environment. Systems must be engineered to create a consistent directional flow away from operators and into filtration zones, without interfering with cranes, tools or operator mobility. For ambient systems, a push-pull configuration or multiple distributed floor units may be used to establish effective circulation.
- Retractable enclosures: In areas where thermal lancing is performed regularly in a fixed location, retractable enclosures such as the DuroRoom™ can provide a semi-contained environment for more effective dust and fume control. These flexible enclosures help contain airborne contaminants and heat while allowing access for equipment and personnel. Combined with properly sized filtration systems, they can significantly improve air quality and simplify compliance.
RECOMMENDED SOLUTIONS
TOTAL FILTRATION PARTNER
RoboVent is your full turnkey resource for clean air in industrial environments. From facility testing and engineering, to installing equipment, providing replacement filters and preventive maintenance, RoboVent is ready to manage the whole process.
CONTACT US
Contact one of our industrial dust experts to gain the advantage against dust-generating processes and applications.