Industrial Hoods and Enclosures
Manufacturing Process Containment and Source Capture
Effective fume control starts with the hood. RoboVent’s industrial hoods and source capture systems control dust, fumes and overspray at the point of generation, keeping your facility cleaner, safer and fully compliant. From modular and retractable process enclosures to receiving hoods and close-capture solutions, RoboVent applies ACGIH industrial ventilation principles to ensure maximum system efficiency, lower airflow requirements and reliable performance.
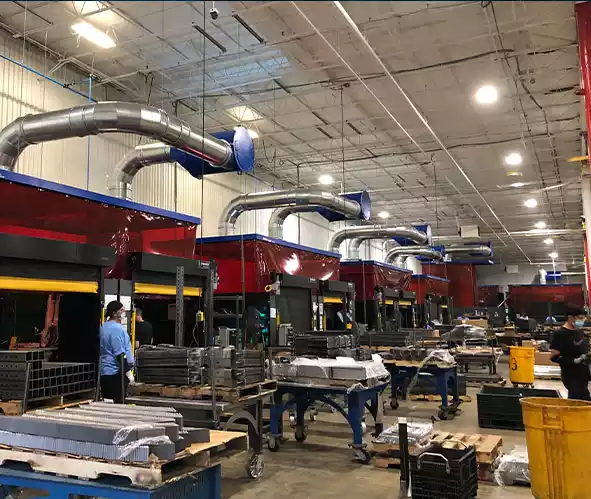

Proven Source Capture Solutions for Cleaner, Safer Manufacturing
A well-designed hood is the foundation of effective fume control, capturing contaminants before they circulate through your facility. The right hood reduces energy demand, improves working conditions, and helps your operation stay compliant without slowing production.
- Protect workers and equipment by controlling dust, fumes, and overspray directly at the source.
- Improve air quality and visibility throughout the facility by preventing contaminant spread.
- Reduce energy use and HVAC load with targeted, right-sized source capture engineered for your process.
- Simplify compliance with OSHA air quality standards and worker safety regulations.
- Accelerate installation and changeovers with modular systems that integrate quickly and minimize downtime.
- Support flexible production with source capture solutions that adapt easily to new layouts, processes and automation.
Enclosure Hoods
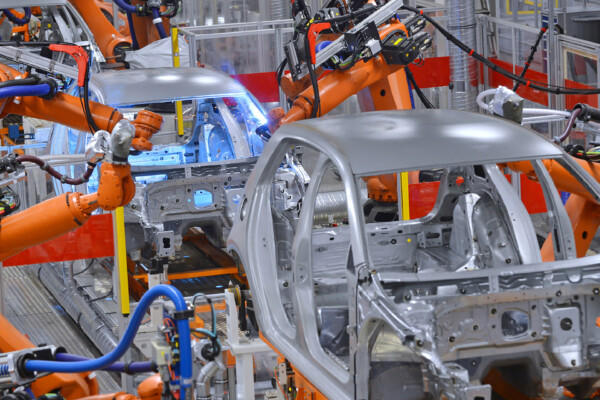
Enclosure hoods provide the highest level of process containment, fully or partially surrounding the work area to capture dust, fumes, mist, and overspray at the source. These hoods are ideal for robotic welding cells, thermal processes, coating operations, and large-part manufacturing where maximum fume control and airflow efficiency are essential. By confining contaminants inside a defined space, enclosure hoods dramatically reduce airflow requirements and improve system performance.
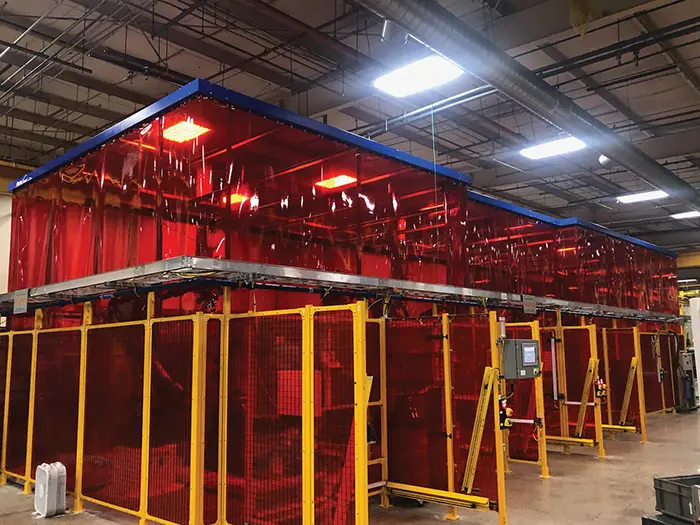

Streamline Hood
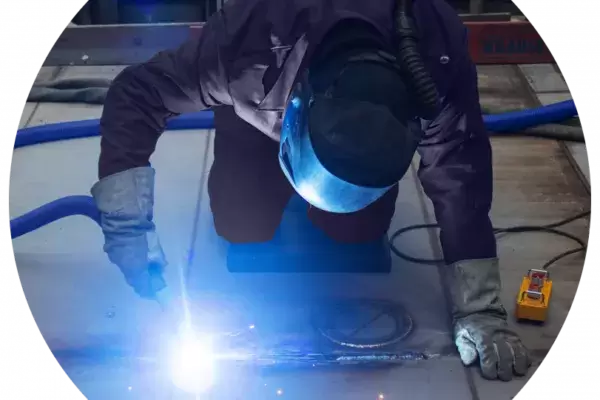
ROBOTIC WELDING HOOD
A streamlined, modular hood system for effective source capture of dust and fumes from robotic welding and other dirty processes.
- Optimized for robotic welding and industrial process containment
- Modular design integrates with robotic systems
- Proven clean-air performance for high-production lines
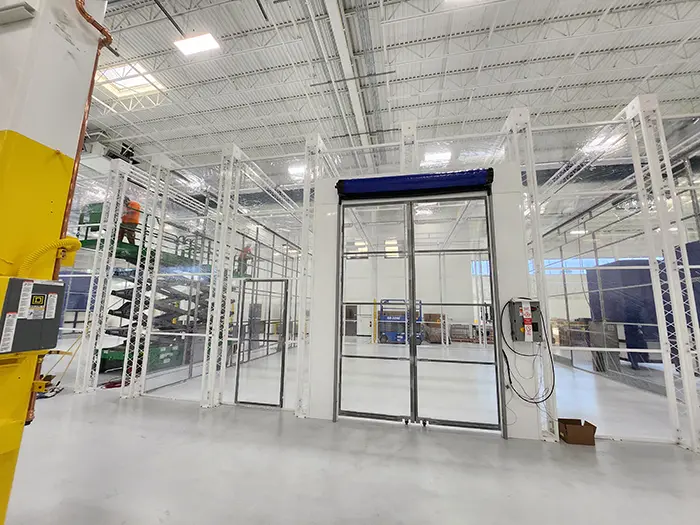

DuroRoom™
RETRACTABLE INDUSTRIAL ENCLOSURE
A flexible process containment system engineered to accommodate large parts, overhead crane use and dynamic industrial workflows.
- Retracts to 20% of full length for crane access
- Configurable for large parts and flexible manufacturing environments
- Code-compliant clean-air control for diverse processes
Proven Source Capture Solutions for Cleaner, Safer Manufacturing
A well-designed hood is the foundation of effective fume control, capturing contaminants before they circulate through your facility. The right hood reduces energy demand, improves working conditions, and helps your operation stay compliant without slowing production.
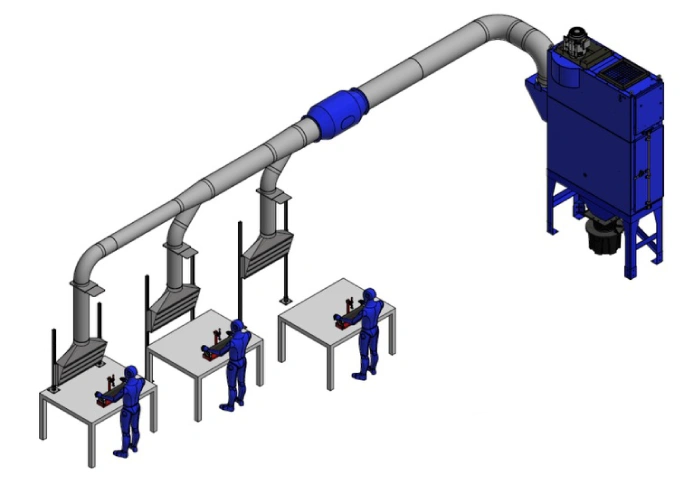

EXTRACTION ARMS
Extraction arms (fume arms) are a versatile and simple solution for capturing smoke, fumes and dust from welding, grinding and other industrial processes. Extraction arms can be ducted to a centralized dust collector or mounted to a mobile fume extraction unit.

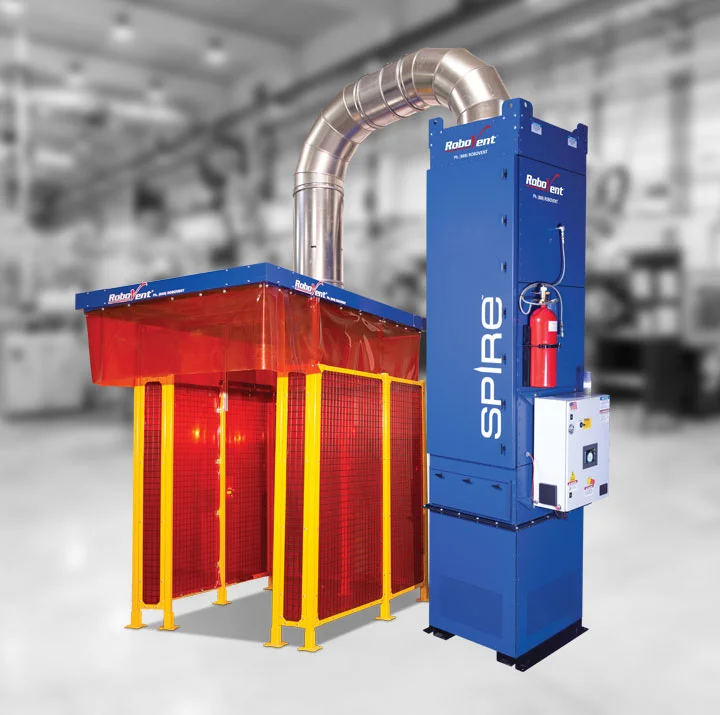
BACKDRAFT AND CROSS-FLOW HOODS
Backdraft hoods capture dust, fumes and mist by pulling air horizontally across the work surface into a slotted or perforated plenum. They provide efficient close-capture for bench welding, grinding, sanding, and small-part fabrication without obstructing operator access.

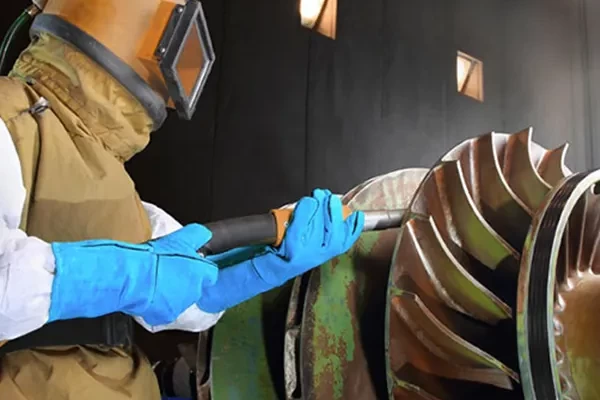
FLEXTRAC™ ROBOTIC FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEM
Control robotic weld fumes at the source with high-efficiency robotic tip extraction. On-torch weld fume extraction is a simple and versatile solution for robotic welding applications that cannot be fully contained.
Receiving Hoods
Receiving hoods rely on the natural movement of rising or outward-moving contaminants, “receiving” fumes, smoke, or dust into the hood opening. They work well for bench welding, cutting tables, grinding operations, and heated processes where emissions follow a predictable path. Receiving hoods provide effective source capture in applications where full enclosures or close-capture devices are not practical.
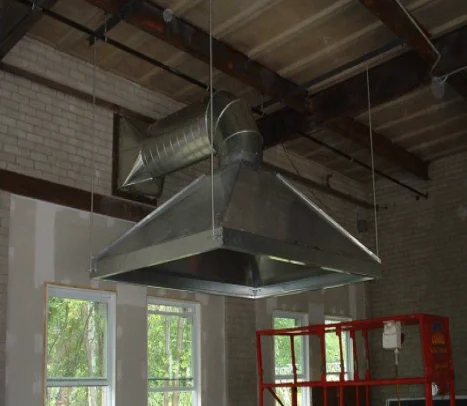

BENCH OR TABLE-MOUNTED RECEIVING HOODS
Positioned above or behind small workpieces to capture rising weld fumes, smoke, or grinding dust.
OVERHEAD RECEIVING HOODS
Suspended above larger processes where heat or plume motion naturally lifts contaminants upward.
SLOTTED OR PLENUM-STYLE RECEIVING HOODS
Use long, narrow openings to capture fumes along a wider work area such as grinding tables or cutting stations.
MACHINE-MOUNTED RECEIVING HOODS
Installed at the discharge or heat source on equipment where emissions move predictably into the hood.
Which Hood Type is Right for You?
Choosing the right hood depends on your process, part size, contaminant behavior, and airflow requirements.
- Choose Enclosure Hoods when you need maximum containment, large-part handling, or lowest energy use.
- Choose Close-Capture Hoods when the operator needs hands-on access or the source moves frequently.
- Choose Receiving Hoods when the process produces a steady upward or outward plume and space is limited.
Use this quick guide to determine which hood style best fits your application.
| Hood Type | Best For | How It Works | Airflow Requirements | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enclosure Hoods | Robotic welding, thermal processes, coating, sanding, large-part manufacturing | Fully or partially surround the process to contain contaminants inside a defined capture zone | Medium airflow: lower than open processes but higher than close capture | High containment efficiency; supports large parts; minimizes fugitive emissions; ideal for automated processes |
| Close-Capture Hoods | Manual welding, grinding, sanding, small-part fabrication, high-motion robotic work | Positioned close to the source to pull contaminants directly into the hood opening | Lowest airflow: highest efficiency due to proximity to the source | Most energy-efficient; operator-friendly; excellent for hands-on tasks or moving sources |
| Receiving Hoods | Bench welding, cutting tables, grinding, heated processes with strong upward plume | Capture contaminants that naturally rise or move toward the hood | Airflow varies based on hood design and proximity to fume source | Simple, economical; effective when plume direction is predictable; minimal obstruction |
The Importance of Effective Hood Design
Well-designed hoods are the foundation of an efficient industrial ventilation system. The hood determines how contaminants enter the system, how much airflow (CFM) is required, and how effectively the dust or fume collector can perform. Proper hood geometry and sizing can reduce required airflow by multiples, dramatically lowering energy use, operating costs and strain on dust collection and HVAC systems. Poorly designed or improperly placed hoods, by contrast, allow contaminants to escape, increase system demand and compromise air quality and compliance.
RoboVent applies ACGIH industrial ventilation principles to every hood we design, ensuring the right hood type, proper sizing and optimized capture velocity for each process. Our engineering team evaluates contaminant behavior, process energy, operator access needs and facility constraints to deliver clean-air systems that perform reliably and efficiently.
Key Considerations in Hood Selection and Design
- Process type and energy: Welding, cutting, grinding, coating and thermal processes each release contaminants differently.
- Capture velocity requirements: Heavier dusts and larger particles generally require higher capture velocities to overcome mass and inertia, while fine fumes or thermal plumes may be captured with lower velocities if their natural upward movement aids the hood.
- Distance from the source: Even small changes in hood-to-source distance can dramatically increase airflow needs.
- Containment vs. accessibility: Balancing enclosure efficiency with operator access and part movement.
- Airflow and CFM optimization: Right-sizing the hood reduces fan horsepower, duct size, and operational costs.
- Part size and orientation: Large or awkwardly shaped parts may require enclosure hoods or retractable designs.
- Plume direction and thermal rise: Essential for choosing between receiving and close-capture solutions.
- Integration with dust collectors: Ensuring airflow, duct routing, and static pressure are engineered as a system.
Integrated Clean-Air Solutions for Complete Process Control
RoboVent's industrial hoods and enclosures are designed to work seamlessly with our advanced dust and fume collection systems-creating a complete solution for clean, compliant air. From source capture to filtration and recirculation, every system is engineered to deliver safety, efficiency, and performance in demanding manufacturing environments.
- Seamless integration: Connect hoods and enclosures directly to RoboVent dust and fume collectors for efficient, end-to-end air management.
- Energy-efficient design: Recirculating clean air reduces HVAC load and overall operating costs.
- Smart control options: Automated airflow monitoring helps maintain consistent performance and compliance.
- One trusted partner: RoboVent engineers and supports the entire clean-air system, from design through installation and service.

Frequently Asked Questions
Industrial Hoods
What are industrial hoods and enclosures used for?
Industrial hoods and enclosures are used to capture dust, fumes, mist, and overspray directly at the source—a method known as source capture. By isolating processes that generate airborne contaminants, these systems protect workers, improve air quality, and support OSHA and NFPA compliance. They’re commonly used for robotic welding, cutting, grinding, painting, coating and large-part manufacturing, where controlling emissions at the source is critical for safety and efficiency.
How do I know which hood type I need—enclosure, close capture, or receiving?
The best hood type depends on how the process generates contaminants. Enclosure hoods deliver the highest containment for automated or large-part processes. Close-capture hoods—including fume arms, FlexTrac™ and backdraft systems—offer the most efficient capture for manual, small-part, or high-motion work. Receiving hoods are effective when the plume rises or moves naturally toward the hood. RoboVent engineers evaluate your process energy, part size, plume behavior, and airflow needs to ensure the hood is properly matched and sized for maximum efficiency.
Can enclosure hoods be used for manual welding and other manual processes?
Enclosure hoods are generally not recommended for manual welding or other hands-on processes, because enclosing a worker inside the hood can trap fumes in the breathing zone and reduce visibility. These systems are designed primarily for robotic, automated, or high-energy processes where the operator is outside the enclosure.
For manual welding, grinding, or fabrication, close-capture solutions—such as fume extraction arms, backdraft hoods and portable source-capture units—provide much safer and more effective control. These devices remove fumes directly at the arc or work surface without restricting operator movement.
If a manual process must occur inside an enclosure (for shielding, airflow control, or process requirements), the hood must be engineered specifically to protect the operator, with properly placed capture points and sufficient airflow to keep fumes out of the breathing zone. RoboVent engineers can help evaluate the process and design a safe, compliant solution.
Why is proper hood sizing important?
Hood size directly affects airflow demand, containment efficiency, and system cost. A hood that is too small allows contaminants to escape; a hood that is too large requires unnecessary airflow (CFM), increasing fan horsepower and energy use. Proper sizing ensures the hood captures fumes at the minimum airflow required—reducing operating costs and improving overall system performance. RoboVent uses ACGIH ventilation principles and process-specific engineering to size hoods precisely for each application.
How do industrial hoods integrate with dust and fume collectors?
The hood defines the capture zone, while the dust or fume collector provides the airflow needed to pull contaminants into the system. Effective system design requires matching the hood type, size, and placement with the correct airflow, duct routing, and filtration technology. When engineered together, the hood and collector work as a unified system—improving capture efficiency, reducing energy use, and maintaining clean, compliant air. RoboVent specializes in designing complete, integrated systems for optimal performance.
What is a receiving hood?
A receiving hood is an industrial hood designed to capture fumes, dust or mist as they rise or move naturally from a process. Unlike full enclosures, a receiving hood sits above or near the source and “receives” contaminated air into the hood opening, where it can be pulled into a dust or fume collector.
Receiving hoods are commonly used for welding, cutting, grinding and small-part fabrication where full containment isn’t practical. They create a defined capture zone that improves air quality, protects operators, and reduces the spread of contaminants throughout the facility.
When should I use a receiving hood vs. a fume arm?
Use a receiving hood when the workpiece stays in a fixed location and the process consistently generates fumes, dust, or mist in a predictable direction—such as welding or grinding small parts on a bench. Receiving hoods provide a stable capture zone without requiring the operator to reposition the equipment.
A fume extraction arm is better for manual or variable work where the operator moves frequently or the weld plume changes position. Arms allow precise, close-range source capture by positioning the hood directly at the point of generation. They are ideal for rework, repair and maintenance tasks where flexibility and mobility are critical.
What’s the difference between a receiving hood and a backdraft plenum?
A receiving hood sits above or in front of the work area and relies on upward or outward air movement to “receive” fumes, dust or mist into the hood opening. It works best when contaminants naturally rise (such as smoke from welding or grinding) and when the workpiece remains in a consistent location.
A backdraft plenum, on the other hand, pulls air horizontally or diagonally across the work surface, drawing contaminants away from the operator and into a slotted or perforated capture panel behind the part. This creates a more controlled capture zone and is ideal for bench welding, grinding and sanding, and fume-intensive small-part fabrication.
In general:
- Receiving hoods are better for lighter fumes or processes that naturally vent upward.
- Backdraft plenums offer more aggressive, directional capture for processes requiring stronger control or closer proximity to the workpiece.
How do industrial hoods and enclosures help meet air quality and safety regulations?
Industrial hoods and enclosures help manufacturers meet OSHA, NFPA and NESHAP requirements by containing airborne contaminants at the source and controlling the spread of fumes, dust, and overspray. By isolating emission-producing processes, they prevent pollutants from entering workers’ breathing zones or accumulating in the facility air.
When connected to a properly engineered dust or fume collection system, these enclosures capture and filter hazardous particulates before clean air is recirculated. This not only supports regulatory compliance but also improves visibility, reduces fire risk and creates a healthier, more efficient work environment.
What are retractable industrial enclosures used for?
Retractable industrial enclosures are used to create clean, controlled work environments for large-part manufacturing, finishing and maintenance processes. They’re ideal for operations that require overhead crane access, flexible layouts or temporary containment, such as painting, coating, sanding, non-destructive testing and heavy-equipment repair.
Because the enclosure can retract to a fraction of its full length, it allows easy material handling and space optimization while maintaining code-compliant air quality and process containment. When paired with dust and fume collection systems, retractable enclosures provide a complete source-capture solution for clean-air manufacturing.
What should you look for in a robotic welding enclosure?
Choosing the right robotic welding enclosure is essential for effective fume control, operator safety, and production efficiency. The enclosure should be designed to contain fumes and mist at the source while maintaining access for robots, tooling, and maintenance. Key factors to consider include:
- Modular construction: Look for a modular design that can be sized or resized to fit your exact process. Right-sizing the enclosure minimizes airflow and energy requirements while simplifying future reconfiguration.
- Fast, easy setup: Systems that assemble quickly with standard tools reduce installation time and production downtime.
- Low-profile design: Compact enclosures save valuable floor space and make it easier to position adjacent cells or equipment.
- Effective fume and mist containment: Proper airflow and sealing prevent fume migration to adjacent work areas, protecting both employees and nearby processes.
- Integration with fume collection: The enclosure should connect easily to ductwork or integrate directly with a dust or fume collector for efficient source capture and filtration.
- Lighting and visibility needs: Consider whether your process requires a light-tight enclosure—such as for laser welding—or benefits from clear panels that allow light and visibility into the cell.
What kind of process containment system can be used for large parts?
Large or irregularly shaped parts often require a retractable industrial enclosure that can expand or contract to match the size of the workpiece. These enclosures provide clean, controlled environments for coating, sanding, grinding, and maintenance of oversized components—such as turbine blades, railcars, or heavy equipment—where fixed booths or hoods aren’t practical. A retractable design allows overhead cranes and lifts to move freely while maintaining compliance with air quality and safety standards.
I use overhead cranes in my facility—what kind of enclosure can I use?
Facilities that rely on overhead cranes benefit from retractable process enclosures that open and close as needed. These systems can retract to a fraction of their full length, providing complete access for cranes and material handling equipment, then extend again to contain dust, fumes, or overspray during production. This design supports both operational flexibility and environmental control without requiring permanent structural changes.
What is the best type of enclosure for coating and painting?
For coating, painting, and finishing operations, the best solution is a process enclosure that isolates the work area, controls overspray, and maintains proper airflow for drying and cure consistency. Depending on part size and workflow, this may be a fixed or retractable system. A retractable industrial enclosure is often preferred for large parts or variable production layouts, providing clean, compliant air while reducing the need for costly ducting and permanent construction.
Ready to build a safer, more compliant workspace?
Talk to our team about air quality solutions built for defense environments—by people who understand the mission.