THE COMPLETE GUIDE TO WELDING
FUME EXTRACTION SYSTEMS:
HOW (AND WHY) TO KEEP YOUR FACILITY AIR CLEAN AND SAFE
CHAPTER SEVEN: OPERATION AND MAINTENANCE OF AIR FILTRATION SYSTEMS
An air filtration system must be properly installed and maintained to ensure that expected results are achieved. This includes:
- System commissioning and validation
- Appropriate filter selection and installation
- Regular filter changes
- Maintenance of the collection system
Operation and maintenance requirements will depend on the type, make and model of the filtration system; always follow the recommendations provided by your owner’s manual for your equipment. The recommendations below are only a general overview.

System Set-up and Validation
System integrity is essential to ensure that the dust collection system is performing as expected. No matter what type of air filtration system you are using, proper setup, commissioning, and system validation will be required. This includes:
- Proper design of the system, including sizing and placement of the collectors, hood and ductwork design for source capture solutions, and analysis of airflow patterns for ambient systems.
- Setup of the filtration device(s) (e.g., dust collector or wet scrubber) according to manufacturer’s specifications.
- Calibration of the system (airflow velocities, etc.) to meet capture rate requirements.
- Validation and testing to ensure that expected capture rates have been met and resulting air quality meets requirements.
Always follow the manufacturer's instructions for your dust collector when installing or replacing filters, and use filters that are designed to the specification of the manufacturer. Using improperly fitting filters or improper installation of filters may result in leaks of contaminants past the filter cabinet, which may put the facility out of compliance.
What kind of spark control is recommended for weld fume extraction?
If welding takes place near the system intake or ductwork, it is advisable to have a method of spark arrestance to prevent a stray spark from igniting the filters. A spark arrestance system is recommended to keep sparks out of the dust collector intake. There are several types of spark arrestors available, including metal mesh screening, centrifugal spark arrestors, and detect-and-suppress systems. A centrifugal spark arrestor, which uses centrifugal force to strip the thermal envelope from sparks, is often recommended for heavy spark-producing applications such as welding. The spark arrestors may be installed inline with the ductwork or at the intake for the dust collection system. Learn more: Spark Control Options for Dust Collection.

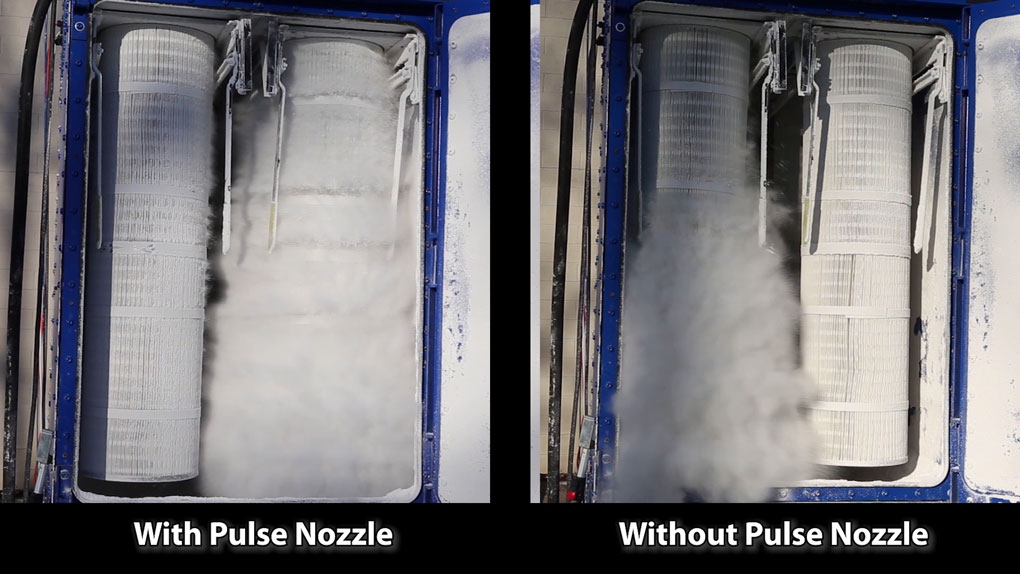
What is a dust collector filter pulsing system?
A dust collector filter pulsing system is a mechanism used to clean the filters in a dust collector. The system uses compressed air to forcefully pulse the filter media, causing the collected dust and debris to fall into a collection bin or hopper. This process is typically automated and can be timed to occur at regular intervals or based on the pressure drop across the filter. Pulsing the filters in this way helps to maintain their efficiency and prolongs their service life. A coated filter media may enable more efficient filter pulsing.
What kind of preventive maintenance is required for dust collectors?
Preventive maintenance is essential to ensure proper continued working of the dust collection system. Maintenance activities and schedules will depend on the type of dust collector you have and the volume of fume you are collecting. For a cartridge-style dust collector, standard maintenance activities include:
- Drum/bin emptying: In a cartridge collector, collected dry particulate falls off the filters and into a tray or bin for collection. When the tray or bin becomes full, it must be safely emptied, and dust must be disposed of in accordance with local regulations.
- Cartridge filter changes: Filters should be changed on a schedule recommended by the manufacturer or when pressure drop across the filter chamber raises by a certain level (specific to your dust collector), indicating that filters have become loaded.
- Spark arrestor cleaning: Mesh-style spark arrestors must be cleaned frequently to avoid buildup of soot from weld fume. Centrifugal spark arrestors should also be cleaned and inspected periodically to remove dust collected in the dust trap or any buildup on the interior walls.
- Filter pulsing system: Check the pulsing system on a regular basis to ensure that it is operational and the compressed air valves have not become clogged.
- Ductwork: Ductwork should be inspected and cleaned on a regular basis to prevent buildup of potentially flammable particulate inside the ductwork.
- General inspection and repair: Regular PM should include inspection of all parts (fans, belts, motor, etc.) to ensure proper operation, and worn or damaged parts should be replaced.
How is weld fume dust disposed of after collection?
Check with local, state, and federal regulations for guidelines on disposing of loaded filter media and collected dust from welding operations, especially if the dust contains toxic byproducts of welding such as chromium, lead or manganese. Safety precautions should be taken by employees when handling dirty filters or emptying dust bins.
- Care should be taken to avoid creating dust clouds when emptying bins for disposal. A vacuum system should be used to clean up any spilled dust.
- Employees should be provided with personal protection equipment (PPE), including gloves, protective eyewear and N95 masks to avoid breathing in or directly touching dust during filter changes and bin emptying.
For more information on weld fume extraction system design, talk to a RoboVent clean air expert.

TALK TO AN EXPERT
Want to learn more? Talk to a dust, mist and fume expert today by filling out the fields below.






